Gas Recovery Retrofit Solutions for Existing Oil & Gas Facilities
Efficient gas recovery solutions for existing oil and gas facilities, combining intelligent management and modular design to reduce emissions and costs, improve energy efficiency with minimal or no downtime, and meet environmental and carbon compliance requirements.

Why Existing Oil & Gas Facilities Are Key Targets for Emissions Reduction
Existing oil and gas facilities represent the majority of operating assets and account for a significant share of energy consumption and emissions. As regulatory focus shifts from new projects to in-service assets, retrofitting existing facilities offers a faster, lower-cost pathway to emissions reduction, often with minimal or no production downtime, making it a key approach to achieving industry decarbonization goals.
Limitations of Traditional Gas Handling Methods
In many existing oil and gas facilities, excess gas is still managed through venting or flaring, leading to wasted energy, higher greenhouse gas emissions, and increased environmental impact. These traditional methods lack flexibility under fluctuating operating conditions and accelerate equipment wear.
As emissions regulations for in-service assets become more stringent, operators are increasingly seeking efficient and controllable gas recovery solutions that reduce emissions, improve operational efficiency, and support long-term sustainability.
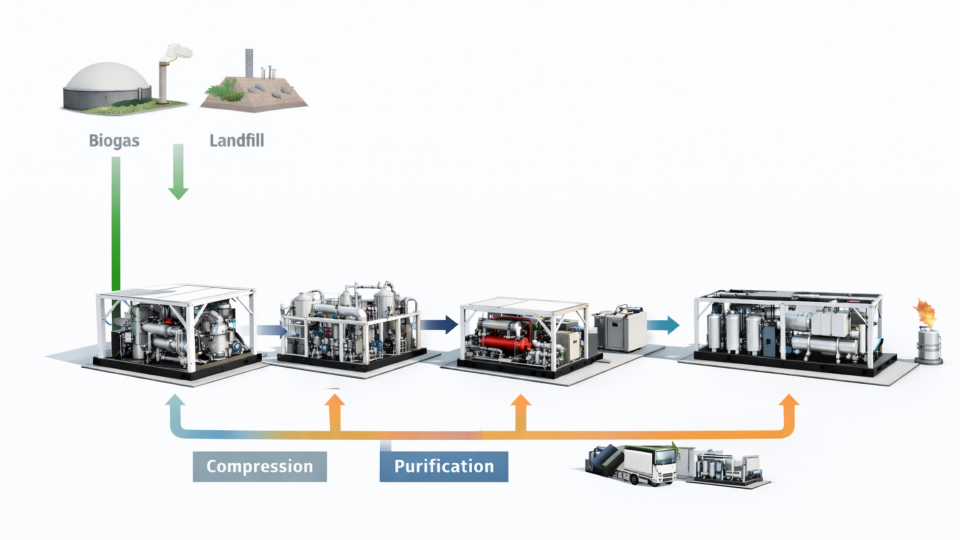
Four Key Solutions for Efficient Gas Recovery
Modular and Skid-Mounted Design
Modular and skid-mounted systems can be rapidly deployed in space-constrained existing oil and gas facilities. Compared with traditional on-site construction, such systems typically reduce overall project delivery time by approximately 30%–60% and cut on-site construction workload by 40%–70%. By completing equipment integration, wiring, and functional testing in the factory, systems can be customized to site conditions while minimizing interference with existing piping, control systems, and operating procedures.
By shifting most manufacturing and commissioning activities to the factory, retrofit projects can often be executed under no-shutdown or minimal-shutdown conditions, significantly reducing construction risks and unplanned downtime. On-site work is largely limited to foundation placement and interface connections, shortening installation time by 30%–50% and substantially reducing construction complexity and site costs.
In addition, modular and skid-mounted systems typically feature standardized expansion interfaces, allowing recovery capacity to be increased or additional modules to be added without extensive modifications to existing systems. This flexible and scalable design enables rapid improvements in gas recovery efficiency, reduces energy losses from venting and flaring, and provides existing facilities with a cost-effective and compliant long-term emissions reduction solution.
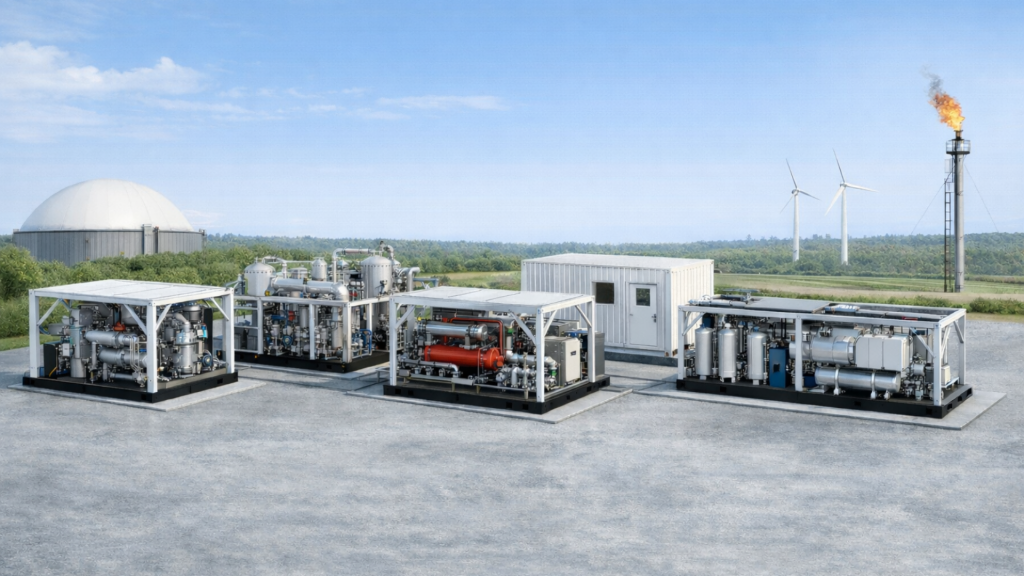

Energy Recovery and Waste Heat Utilization
In KAITIAN GAS’ modular and skid-mounted gas recovery systems, waste heat recovery is treated as a core component of overall energy efficiency optimization and is tightly integrated with compression, purification, and liquefaction processes. Dedicated heat exchangers recover waste heat generated from compressor discharge, refrigeration cycles, and regeneration processes, improving overall energy utilization without increasing additional power consumption.
Recovered thermal energy can be flexibly applied to feed gas or process medium preheating, regeneration of purification absorbents, pipeline freeze protection, and equipment or building heating, effectively reducing reliance on external fuel and electricity. Thanks to the modular design, waste heat recovery units can be configured and expanded based on site conditions and gas volumes, accommodating gas flow fluctuations and different project phases.
By integrating waste heat recovery within skid-mounted systems, KAITIAN GAS achieves a synergistic improvement in energy recovery, emissions reduction, and operational stability. This integrated design reduces specific energy consumption and operating costs per unit of recovered gas, while minimizing the need for additional auxiliary facilities, providing a practical and reliable pathway for energy-saving retrofits under no- or minimal-shutdown conditions.
Intelligent Systems and Remote Operations & Maintenance
By equipping gas recovery units with Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and intelligent control modules, key operating parameters—including gas flow rate, composition changes, pressure, temperature, and recovery efficiency—can be continuously monitored online. These data are transmitted in real time to a central control platform via industrial communication networks, allowing operators to maintain full visibility of system performance without frequent on-site inspections.
Based on real-time data, intelligent control systems can remotely adjust and automatically optimize compressor loads, recovered gas volumes, and bypass ratios, ensuring stable operation under fluctuating gas conditions or changing process requirements. This reduces manual intervention and operational errors while significantly lowering on-site maintenance workload, making the system particularly suitable for geographically dispersed or remote oil and gas facilities.
In addition, by analyzing historical operating data and performance trends, the system enables predictive maintenance capabilities. Early warnings can be issued when pressure anomalies, efficiency declines, or abnormal vibration patterns are detected, allowing maintenance to shift from reactive repairs to planned interventions. This approach effectively reduces unexpected shutdowns and production losses caused by unplanned maintenance.
Gas Separation and Multi-Level Utilization
Modern gas recovery systems combine purification, separation, and conditioning technologies to enable multi-stage gas separation and optimized utilization. Moisture, particulates, and heavy hydrocarbons are removed first, followed by acid gas removal, adsorption, or membrane separation to efficiently separate combustible gas and by-products.
High-value combustible gas can be reused for fuel, power generation, or further compressed or liquefied for sales or peak-shaving, while CO₂, H₂S, and other by-products can be treated, re-injected, or repurposed to meet environmental and compliance requirements. This flexible, multi-level utilization approach improves recovery efficiency, reduces emissions, and maximizes the overall value of recovered gas.
Conclusion
By implementing systematic gas recovery retrofits in existing oil and gas facilities, operators can achieve significant emissions reductions with minimal or no downtime while reducing energy waste and operating costs. Integrated modular design, energy recovery, intelligent operations, and gas separation technologies deliver clear investment returns, support ESG and carbon management goals, and enable long-term sustainable asset performance.