Indonesia’s 2025 Mega Natural Gas Field Discovery Sets New Industry Momentum
One of the largest discoveries of natural gas reserves In the world’s Kutei basin was announced by Eni in the beginning of 2025. This announcement drew the attention of Operational Stakeholders and Policy Makers as well as Energy Transition Analysts. Though the discovery has yet to be evaluated for commercial scale, industry insiders believe the discovery could be the single most important find in Southeast Asia In the past 10 years. The Oil and Gas Journal and Upstream Energy Intelligence believe the discovery could increase Economic Gas Supply Stability and positively change the direction of investment toward the Asian LNG Supply Chain.
3125 Gas Recovery Enhancing Technology Systems is clearly the world’s leader in the field and for this reason the announcement provides a positive signal for sustainable gas capture, flare reduction and improved gas recovery companies. For KAITIANGAS this has great strategic importance as well.
A New Development of Southeast Gas Globally Positioned Southeast Asia Gas Market
The Kutei Basin is Indonesia’s most promising deepwater natural gas prospects. The basin’s geological structure is complex. In the basin there have been several rounds of seismic acquisition and stratigraphic studies along integrated well and seismic analyses. These studies have indicated the sign of thick and continuous gas reservoirs and of excellent reservoir properties. The initial technical disclosures issued by Eni describe the new well succeded in discovering stratigraphic sandstone composition of high quality. In addition, there are logging and testing data of stable flow rates of gas which shows the site has great commercial potential.
Under the new gas discovery in the region, several energy institutions, and in particular the media energy, describe the new discovery as a potentially major gas supply and demand disruption in Southeast Asia. This is primarily due to a number of structural trends pushing countries to revise their gas supply strategies as well as expedite oil and gas upstream activities.
Asian LNG Demand Expansion
For the last five years, Asia has been the main driver for the incremental global LNG demand. According to the IEA’s report and other industry studies, East and Southeast Asia’s consumption of natural gas has been growing at an average of approximately 3 to 5 percent yearly. Simultaneously, developing nations like the Philippines, Vietnam, and Bangladesh are in a hurry to build their first LNG receiving terminals to supplant their energy requirements. The demand for natural gas in the region has been very inelastic due to gas being substituted in other industries, power sector reformation, and the implementation of coal use reduction policies in some countries.
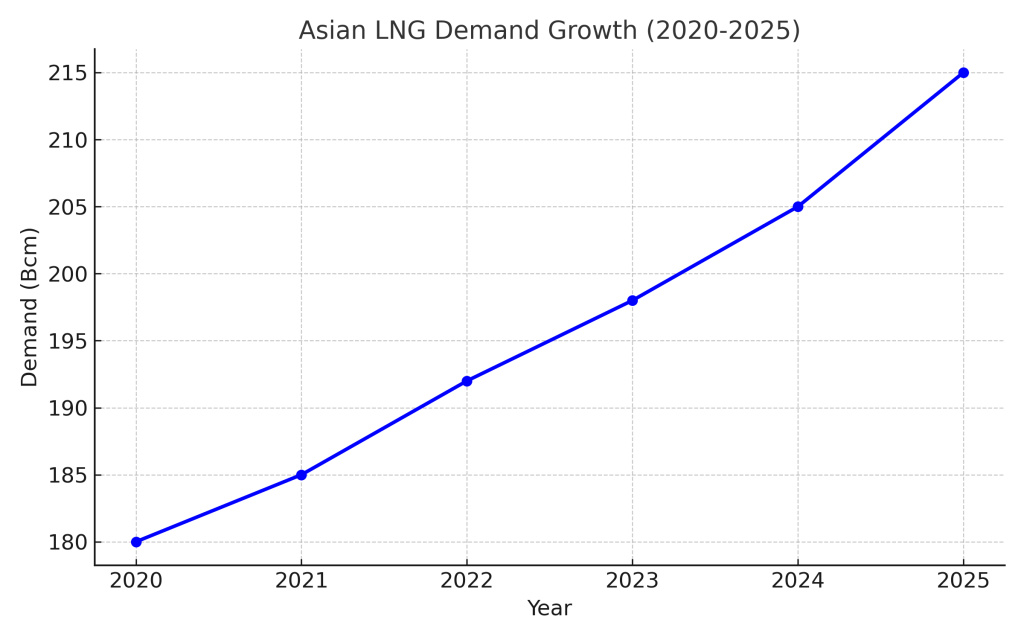
Against this backdrop, natural gas production capacity in Southeast Asia has been declining over the years. Hence, the Kutei Basin in Indonesia has been a growing supranational centre of interest and will provide the local industry with the supply of gas it desperately needs. It will also become a potential major incremental outlet to the region’s natural gas supply.
The Importance of Energy Security
Over the last couple of years, most of the world’s major energy importing countries have started considering the security of their natural gas supply chain. Volatility in the geopolitics of the world, the instability of international gas spot prices, and the increased costs of transporting gas over long distances, have led countries to focus more on the gas supply that they can control in their own regions.
For Southeast Asian countries, the long-term ‘scissors gap’ of the region’s production capacity declining and the demand increasing, in combination with frequent fluctuations in the spot price of gas, has been the most dominant for countries sensitive to the cost of generation. At the same time, there is a general proposal for the regions governments to have a more diversified supply, and for policies to address self sufficiency in energy, to be put in place.
With that in mind, the recent discovery of a sizeable gas field in Indonesia is not only new economically, but to the entire Southeast Asian region, its supply security is of great strategic importance.
Reduction in Production From Old Oil and Gas Fields
Most of Southeast Asia’s gas fields are in advanced stages of pressure depletion and recovery. According to the region’s upstream regulators, Indonesia and Malaysia’s gas fields are experiencing 8 to 12% declines in production annually. More classic offshore gas fields in Vietnam and Brunei are also experiencing declines. The continued production of aging infrastructures at facilities with high operating costs are also factors that are producing some pressure on the region’s gas supply.
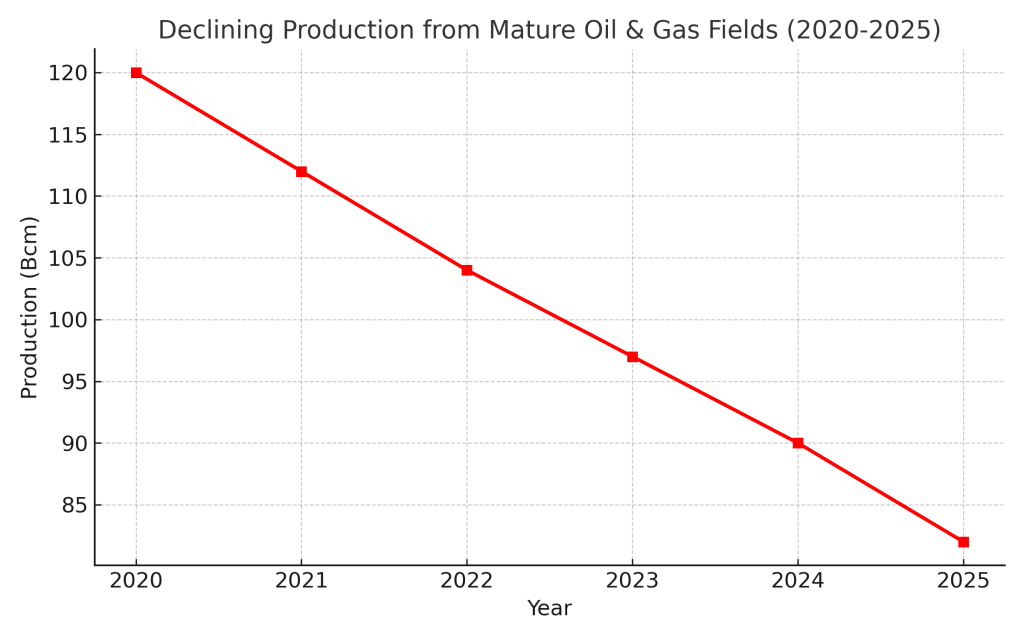
In this context, the region’s newly explored mid-size to large gas fields will be a major “structural pillar” of the supply of gas over the next 10 years. The recent, and massive discovery of natural gas in Indonesia will be a major contributor of gas supply to the entire Southeast Asia region.
The Government Encourages Development of Natural Gas and its Infrastructure
The Indonesian government has been working hard to encourage the growth of naturally occuring natural gas. The deadweight gas fields, ,’ and configuring, has been massive. Furthermore, the government has been looking to implement strategies to better optimize the gasses, focuisng on its the fuel gasses importance.
The discovery of the Kutei Basin gas reserve will allow gas with policies to be issued and gas recovery and retention with the fuel emissions to optimize quickly. It will create more opportunities for the gas industry to be optimized.The discovery is not the bore, but of great importance to the natural gas industry and it’s efficiency. This has great use gas, but will allow the large industry with tech to more with its natural gas supplies.
What Drives the Demand for Advanced Gas-Recovery Solutions Following the Indonesia Discovery
While the Indonesia discovery may seem groundbreaking, it does not improve the commercial viability of the segment. Producing gas from the portion of the reservoir governed by the discovery comes with new hurdles from regulators and investors. Expectations from SKK Migas as Indonesia’s upstream regulatory body and overseas financiers include:
Improving Natural Gas Capture Efficiency: Creaming The Waste Of Flaring Gas
While gas fields are in their early production stages, their associated gas, or low-pressure gas, if not efficiently captured, tends to be flared or vented. This not only wastes the gas, but also leads to higher emissions. The International Energy Agency and the World Bank’s Global Gas Flaring Reduction report states that hundreds of billions of cubic meters of gas are still being vented or flared each year throughout the world.
Operators not having to vent or flare gas should have the following:
- A gas recovery system that is able to quickly capture associated gas and convert it to marketable gas or energy is essential.
- Early production stage (EPS) modular equipment is needed that can be rapidly deployed and that can be connected easily to available platforms or pipelines.
- Every opportunity to convert potential waste to economic value should be seized.
Increased efficiency of the capture of natural gas fulfills the requirements of the market and leaves the operators with no emissions regulatory hurdles. This is also a huge step in the world towards meeting the emission reduction requirements of governments and financial institutions. ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance) compliance.
Lessening Production Carbon Intensity: International ESG Goals
The exploitation of new natural gas fields must satisfy national and international environmental obligations. In recent years, the Indonesian government and large foreign investors have been more concerned with the upstream natural gas operating carbon emission management, and the same emission reduction targets have been established by the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, and the World Bank GGFR.
Implementation targets:
- The introduction of engineering designs aimed at the reduction of flaring and venting.
- The installation of gas recovery equipment made of high operating temperature, corrosion resistant materials to ensure stable operation of equipment.
- The incorporation of automated systems that enable carbon emissions data emission real time recording and reporting.
Most new gas fields will have set emissions reduction management systems that will enable them to low carbon operating standards while primarily mitigating the compliance and the cost of financing.
Enhancing Production Stability to Improve Recovery Rate
Giant natural gas fields are often very complex. They can have several different geological formations. There can also be large differences in pressure within the same field. Production of gas will decline rapidly in the medium to long-term when operators use ultra-conventional methods. This can cause ultimate recovery to be very restricted.
Because of the reasons above, operators in gas fields should use the following:
- Custom gas injection, pressure control, and production optimization methods.
- Real-time pressure and production control.
- Long-term production decline management to low the rate of recovery in the gas field.
This in an effort to reduce the production decline rate. This ensures that gas fields of economic value will have long-term high value.
Recovery Efficiency is Important for Public Natural Gas Field Supervision
Global Gas Analytical Agencies assert that the long-term gas field development must include an area for Recovery Efficiency as one of its objectives because there is no long-term development that can include no attention to Recovery Efficiency. Integrated Efficient Soft Ware and Gas Capture and Recovery with Low Emission Enhanced Recovery will be the norm for Upstream Projects to come.Overall Indonesia will further gas technological innovations for the gas Recovery and widespread use of Enhanced Gas Release Engineering corrosion Control and modular Engineering. Low Emission gas engineering for End of 2025 will be strategically important for Efficiency of the Zone and to set a new phase for Upstream Natural Gas Development that will focus on the long term recovery of the environment.
How KAITIANGAS Powers Industry Momentum
As large-scale discoveries reshape regional supply dynamics, KAITIANGAS provides operators with solutions that are aligned with the next era of gas development:
High-Efficiency Natural Gas Recovery Systems
High-efficiency natural gas recovery systems can capture excess associated gas and low-pressure gas within production phases and save gas from being wasted through flaring and sell it as convertable energy or as a service with products on-site. These systems also have a modular design for fast paced commissioning and offer compressional liquefaction or power generation and also enable operability for remote automated control.
On a wider scale, high-efficiency natural gas recovery systems greatly enhance operational cash flow from initial gas production and emission control and regulatory compliance combined with investor satisfaction make it a highly strategically operational systems within new gas fields.
Enhanced Recovery Technologies
Mature gas fields can have their recovery rates improved through Economic lifetime extensions via injection-production optimization, pressure control, intelligent reservoir control, etc. Technologies tailored multi-layered gas reservoirs, reservoirs with complex pressure gradients, and areas with high production are also designed for. Optimally these allow the industry to avoid mature gas fields unsustainably, enjoy long and stable production, avoid unsustainably high costs on development, and financially benefit overall.
Modular, Corrosion-Resistant, and High-Temperature Engineering Equipment
This device is capable of being used in complex offshore platforms and high-faulted or high-sulfur gas fields, which makes it highly versatile and allows for the use of high-stable long-term operations. Some of the tech of which include modular units for quick and easy installation and expansion, as well as high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance. All of which are guided by international standards. At this level of the industrial sector, this device makes it possible and safe to fully unlock the potential of complex reservoirs, as well as allows for rapid, safe, and low-risk commercial operations.
Systematic Design Aligned with Corporate Emissions Reduction Goals
This system incorporates natural gas recovering, Enhanced Gas Recoveries (EGR) and, on site monitoring to attain an optimal level of control of carbon and methane emissions. It works best for an early start-up of new gas fields, long term stable production periods, and multi-phased production cycles. At the industry level, the system allows operators to meet and exceed domestic ESG and international compliance/Investor grade requirements enabling a compliance-commercial value-win.
When made accessible, natural gas discoveries, like the Kutei Basin in Indonesia, is not only an economic boon for an operator, KAITIANGAS’s technological solutions have moved from beneficial to compulsory. It allows the operator to efficient and economically developed while supporting the industry’s strategy in emissions conservation, reduction and environmental compliance. It also moved the entire natural gas development ecosystem in to greater developed efficiency and sustainable.
Looking Ahead
The Kutei Basin 2025 discovery is the start of a new chapter in the region’s energy landscape, emphasizing the strategic role of natural gas development. Today, the value of gas fields goes beyond just the reserves, but rather the lifecycle recovery efficiency, emissions captured, and if recovery is enhanced. The ability to capture associated gas early in the field development cycle, if Enhanced Gas Recovery (EGR) is deployed in the mature fields in combination with compliant and reliable engineering tools, determines field development success. This is true not just for Indonesia, but for the rest of Southeast Asia and even the entire upstream of the world. This is demanding for new technologies and for a new way to manage and lead systems.
For KAITIANGAS, in this context, is one of the most empowering of these high-efficiency, low-emission, and sustainable gas development enablers. KAITIANGAS integrates high-efficient gas recovery, enhanced recovery engineering tools and high-quality engineering to deliver economic output, energy supply security at the regional level and enables energy transition. With the coming of more mega gas fields, the natural gas industry will be defined by technologies and practices that focus of efficiency and recovery.