Modular Shale Gas Liquefaction Plants: Advantages and Application Trends
What is a modular shale gas liquefaction plant?
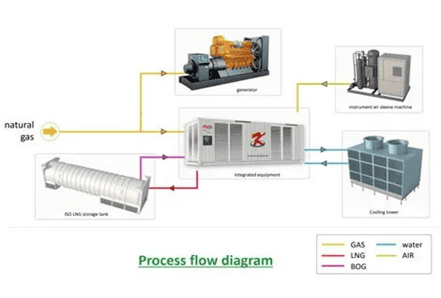
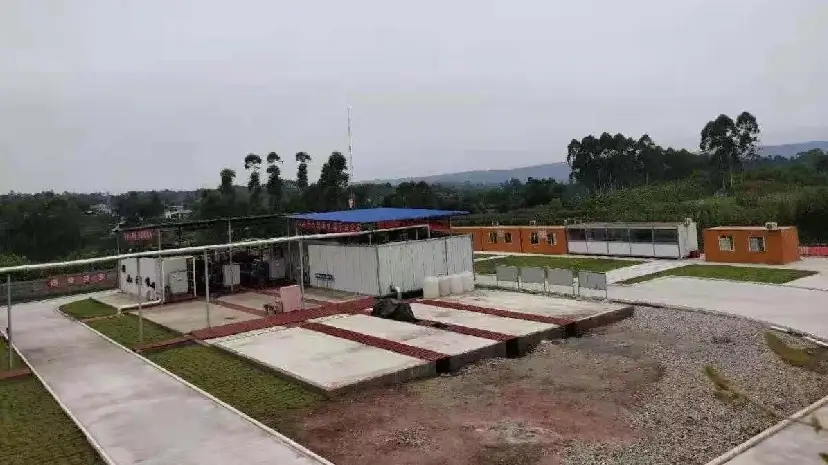
A modular shale gas liquefaction plant is a system that transforms natural gas from a gaseous to a liquid state. It consists of multiple standardized modules covering gas pre-treatment, cooling and liquefaction, storage, and loading. Compared to traditional, site-built LNG plants, modular units are prefabricated and tested in a manufacturing facility, then transported to the site for rapid assembly and commissioning. This approach significantly shortens the construction cycle, reduces costs, and is particularly suitable for shale gas development in areas with dispersed resources, complex geography, or limited transportation access.
Key Advantages of Modular Shale Gas Liquefaction Plants
Significantly Shorten Construction Cycles and Accelerate Time-to-Production
In the traditional plant construction model, processes such as design, procurement, civil engineering, installation, and commissioning must be carried out sequentially on-site, a process that often takes several years. In contrast, the modular approach utilizes parallel engineering. While land grading and foundation work are underway at the gas field, various process modules (like pre-treatment, liquefaction, and power generation) can be manufactured simultaneously in a specialized factory.
The modules are prefabricated, assembled, and largely tested in the factory, which greatly reduces the workload for on-site installation and commissioning. According to industry experience, the modular method can shorten the time from the final investment decision to the first LNG production by 40% or even more, helping investors achieve cash flow faster and seize market opportunities.
Lower Initial Investment and Project Risk
Shale gas wells are characterized by high initial production rates followed by a rapid decline. The scale of modular plants is flexible and can be “custom-tailored” to the actual production and decline curve of the gas wells, avoiding the risk of idle capacity caused by excessive initial investment. Investors can start with a smaller-scale plant and then easily expand capacity by adding more modules as gas field exploration and development progress and production becomes clearer, effectively diversifying investment risk.
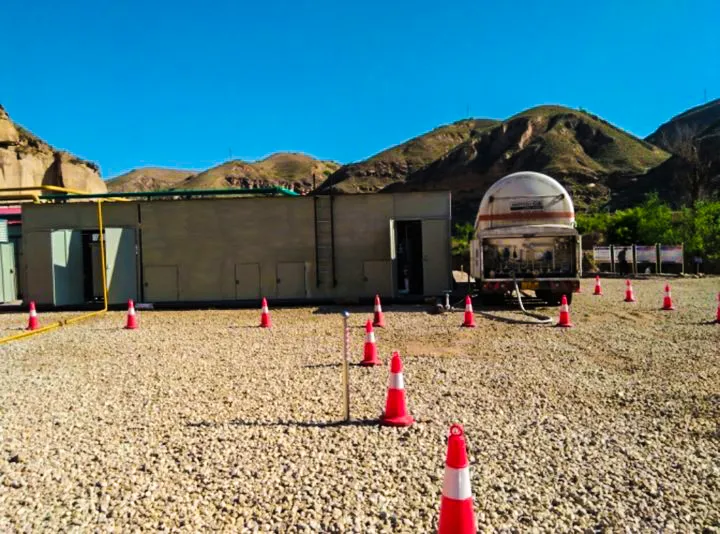
Flexibility and Mobility
While shale gas resources are widely distributed, the production life of a single well pad or small gas field is relatively limited. Modular liquefaction plants are designed to be detachable and transportable. When the gas source in one area is depleted or becomes uneconomical to exploit, the entire plant or its core modules can be dismantled, transported to a new gas field, and reassembled for production.
This “nomadic” production capability maximizes asset utilization and prevents the issue of stranded assets that occurs with traditional plants, which cannot be moved once built. This is especially advantageous for shale gas production areas that are remote and have poor infrastructure.
Application Scenarios and Future Trends
Application Scenarios

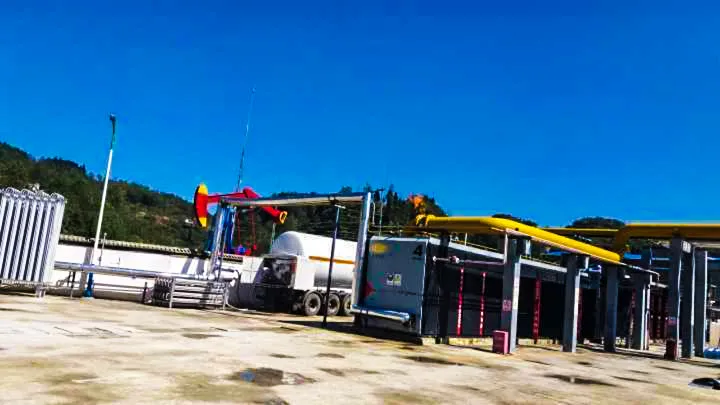
Remote Shale Gas Development: For shale gas fields located far from existing natural gas pipelines, modular plants can liquefy the gas directly at the source. The LNG can then be transported to consumer markets via tanker trucks or small-scale LNG carriers, avoiding the high cost of pipeline construction and improving development efficiency. This is particularly applicable to areas with complex geological conditions and scattered wells.
Recovery and Utilization of Associated and Low-Grade Gas: During oil and gas extraction, associated gas or low-pressure, low-grade natural gas is often produced. For economic or technical reasons, this gas is frequently flared (vented) or wasted. Modular liquefaction units can effectively collect and liquefy these dispersed gas sources, turning waste into a valuable resource and reducing environmental pollution.
Temporary or Emergency Gas Supply: In cities, industrial zones, or remote communities, modular liquefaction plants can serve as a temporary emergency gas source to provide a stable LNG supply in response to shortages or interruptions in conventional gas service.
Peak Shaving Gas Source: During periods of peak natural gas consumption (like winter), urban gas demand surges, and the capacity of traditional long-distance pipelines is limited. Modular liquefaction plants can liquefy and store surplus gas from the pipeline network and then re-gasify it during peak demand, playing a peak-shaving role to ensure supply security.
Distributed Energy Stations: Modular liquefaction units can be integrated with downstream applications like gas-fired power generation and industrial heating to form small-scale distributed energy systems. These systems can provide clean, on-site energy for industrial parks, mines, and rural areas, improving overall energy efficiency.
Future Trends
-1.png)
Diversification of Applications: From a Single Fuel to Comprehensive Utilization
In the future, the application of modular shale gas liquefaction plants will no longer be limited to producing only LNG for vehicle fuel but will evolve in more diverse directions.
- Regional Energy Hubs: In industrial parks, towns, or mining areas not covered by pipeline networks, modular LNG plants can act as small-scale regional energy hubs, providing industrial fuel, residential gas, and gas-fired power generation for the local area.
- LNG Cold Energy Utilization: LNG releases a significant amount of cold energy during regasification. Future modular plants will focus more on the cascade utilization of this cold energy for applications such as cold storage, air separation for nitrogen and oxygen production, and even cold-energy power generation. This will achieve comprehensive and efficient energy use, further enhancing project economics.
- Exploration of Co-production Models: To handle high-value components in shale gas, such as condensate oil and LPG (liquefied petroleum gas), future modular plants will integrate light hydrocarbon recovery units. This will enable the co-production of multiple products like LNG, LPG, and stable light hydrocarbons, maximizing resource value.
Market Demand: Driving Industrial Development
Increasingly Strict Environmental Policies: Strict environmental regulations limit the direct venting of natural gas and impose higher standards on the environmental impact of shale gas extraction. Modular liquefaction plants can effectively recover and utilize associated gas and wellhead gas, reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, modular environmental facilities, such as wastewater treatment, are becoming more mature, providing technical assurance for the green development of shale gas.
Natural Gas Price Reform and Marketization: As market-oriented reforms of natural gas pricing deepen, the sale of wellhead LNG will become more flexible, and its price linkage to the international LNG market will strengthen. This will enable distributed LNG producers to better seize market opportunities and improve profitability, thereby attracting more private capital to invest in modular liquefaction projects.
KAITIANGAS: Your One-Stop Shale Gas Recovery Solution
Founded in 2002, KAITIANGAS is focused on the recovery and processing of shale gas resources. The company specializes in the development, engineering design, and global promotion of shale gas recovery and liquefaction technology and equipment. Kaitian Gas possesses proprietary intellectual property, mature system solutions, and a professional team. We provide end-to-end services from project feasibility consulting and engineering design to EPC execution and commissioning, helping energy producers meet regulatory requirements, achieve sustainable development, and ensure production capacity.
Summary
Modular shale gas liquefaction plants are progressively changing the way unconventional natural gas is liquefied. Their technical advantages of standardization, intelligence, and sustainability are bringing more possibilities to the energy industry. In the face of a complex market environment and the challenge of low-carbon development, modular liquefaction equipment is undoubtedly a more flexible and efficient solution. In the future, with upgrades in manufacturing technology and growth in global energy demand, this technology will be widely applied in more scenarios.
Contact KAITIANGAS—the expert in energy efficiency solutions—and we will provide a customized shale gas recovery plan based on your needs.