What is Coalbed Methane? Development Value Analysis and Corporate Low-Carbon Transition
What is Coalbed Methane?
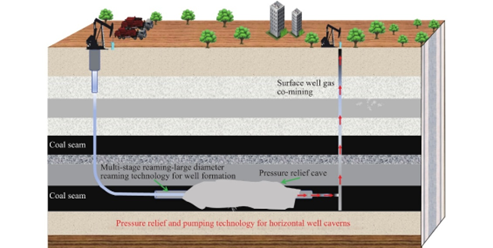
Coalbed methane refers to methane gas contained within coal seams, gradually accumulated during coal formation and tightly bound to the coal structure. Its main component is methane, with a purity of over 90%. As an unconventional natural gas, CBM features high calorific value and low pollution.
Compared with conventional natural gas, CBM development relies more on geological evaluation and directional drilling technology. Unlike shale gas, CBM usually occurs in shallower layers and is relatively easier to extract. More importantly, CBM extraction not only converts gas into energy but also helps prevent coal mine gas explosions, achieving both energy and safety benefits.
Development Value of Coalbed Methane
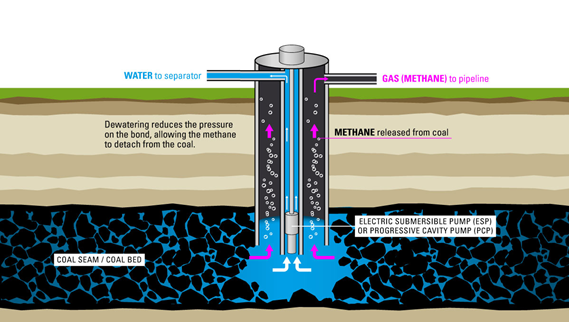
Resource Conversion: Transforming Coal Mine Waste Gas into Energy Assets
Methane naturally formed in coal seams has long been treated as a useless by-product, typically vented or flared, which not only wastes valuable energy but also poses significant environmental risks. Today, with advanced extraction and purification technologies, these previously neglected gas resources can be safely collected and converted into high-calorific, low-emission clean fuels for power generation, heating, or further processed into compressed natural gas (CNG) or liquefied natural gas (LNG), greatly improving energy utilization efficiency.
Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Supporting Carbon Peak Goals
Methane’s greenhouse effect is more than 25 times that of carbon dioxide. CBM recovery can significantly reduce direct emissions, becoming a crucial tool for companies to achieve carbon peaking and carbon neutrality. For energy-intensive enterprises, deploying CBM projects not only cleans up their energy mix but also enables participation in carbon asset trading and access to policy incentives.
How CBM Supports Corporate Low-Carbon Transformation
Clean Energy Substitution: Restructuring the Energy Mix
CBM has high calorific value and low sulfur content, making it an ideal substitute for high-pollution fuels like coal and diesel. Applying CBM to boilers, industrial kilns, and power systems can significantly reduce pollutants and carbon emissions, aiding enterprises in achieving green production.
Enhancing Environmental Compliance
With the deepening of China’s “dual carbon” goals, environmental policy and supervision are becoming stricter. Incorporating CBM into corporate energy planning can significantly improve environmental performance, reduce policy risks, and boost ESG ratings.
Creating Dual Economic and Environmental Benefits
Through CBM development, companies not only secure a stable energy supply but also generate carbon reduction credits (e.g., CCER) for trading in carbon markets, thereby achieving additional revenue.
Typical Application Scenarios of CBM Development
| Application Scenario | Specific Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Coal mining enterprises | Deploy gas extraction and recovery systems to convert gas into onsite fuel or sell as natural gas. |
| Distributed energy projects | Use CBM for local power stations or energy supply in industrial parks. |
| Modular liquefaction plants | Liquefy CBM onsite into LNG for efficient transportation and remote supply. |
| Industrial fuel substitution | Replace diesel and coal-fired boilers to reduce emissions and lower operating costs. |
Economic Feasibility Analysis of CBM Development
Reasonable Payback Period: With the maturity of skid-mounted, highly integrated, and intelligent recovery systems, payback periods for small- and medium-sized CBM projects have shortened to 2–4 years.
Low Operating Costs, High Profit Potential: Stable gas sources and simple maintenance make long-term deployment feasible.
Policy Incentives: Many local governments provide subsidies, tax reductions, and green financing for methane recovery and utilization.
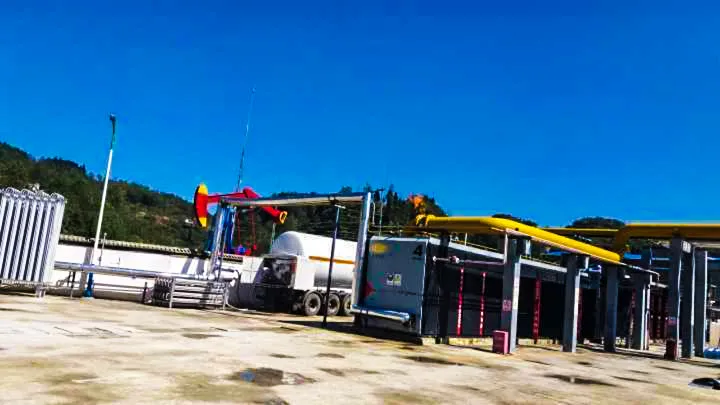
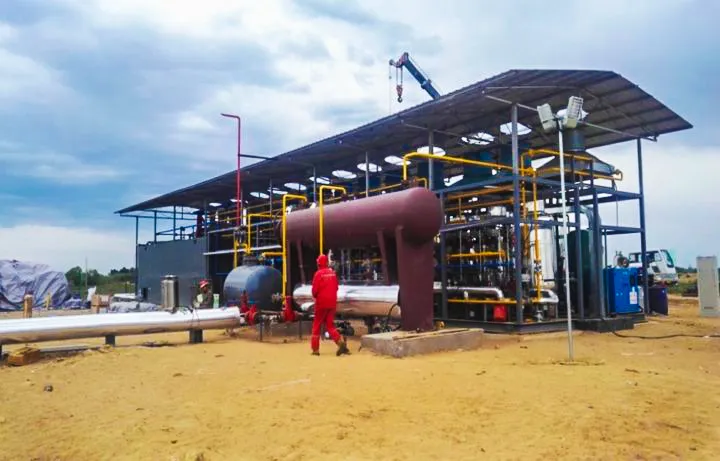
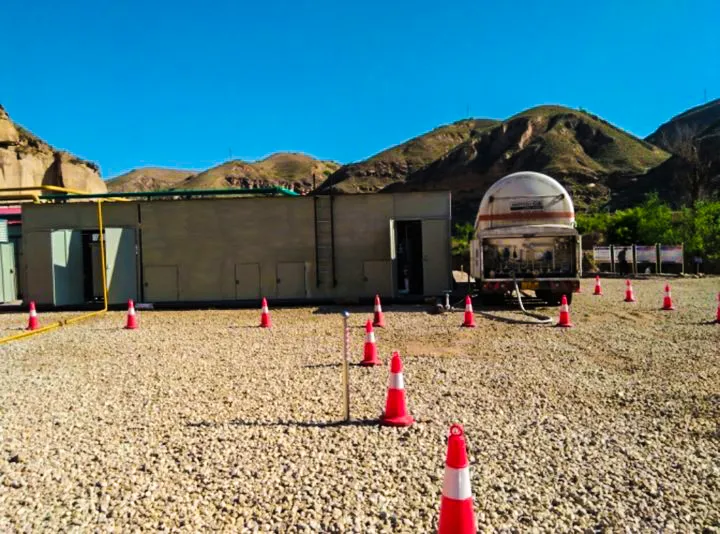
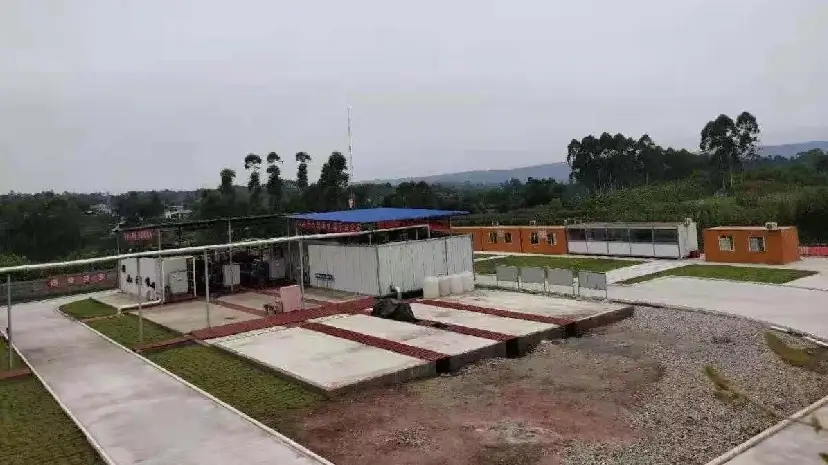
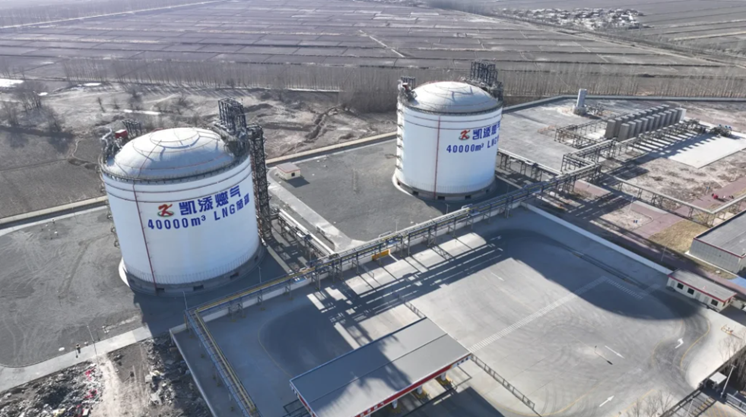
KAITIANGAS One-Stop CBM Recovery Solutions
Founded in 2002, KAITIANGAS specializes in CBM recovery. Addressing the high water content, corrosiveness, and volatility of CBM and mine gas, the company has developed skid-mounted, highly integrated, and intelligent recovery systems tailored to coal mine site requirements. It offers comprehensive services from project consulting, engineering design, equipment manufacturing, EPC contracting, to system commissioning, supporting safe and efficient recovery and centralized processing of multi-well gas sources.

Conclusion
In today’s global transition toward carbon neutrality, companies face unprecedented pressure to green their operations. How to ensure energy supply while reducing carbon footprints is an urgent challenge for energy-intensive sectors. CBM, as a clean, efficient, and economical unconventional natural gas resource, is emerging as a new solution for corporate low-carbon transformation.
Contact KAITIANGAS for customized CBM recovery solutions.