What Is Liquefied Natural Gas Used For
What is Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG)?
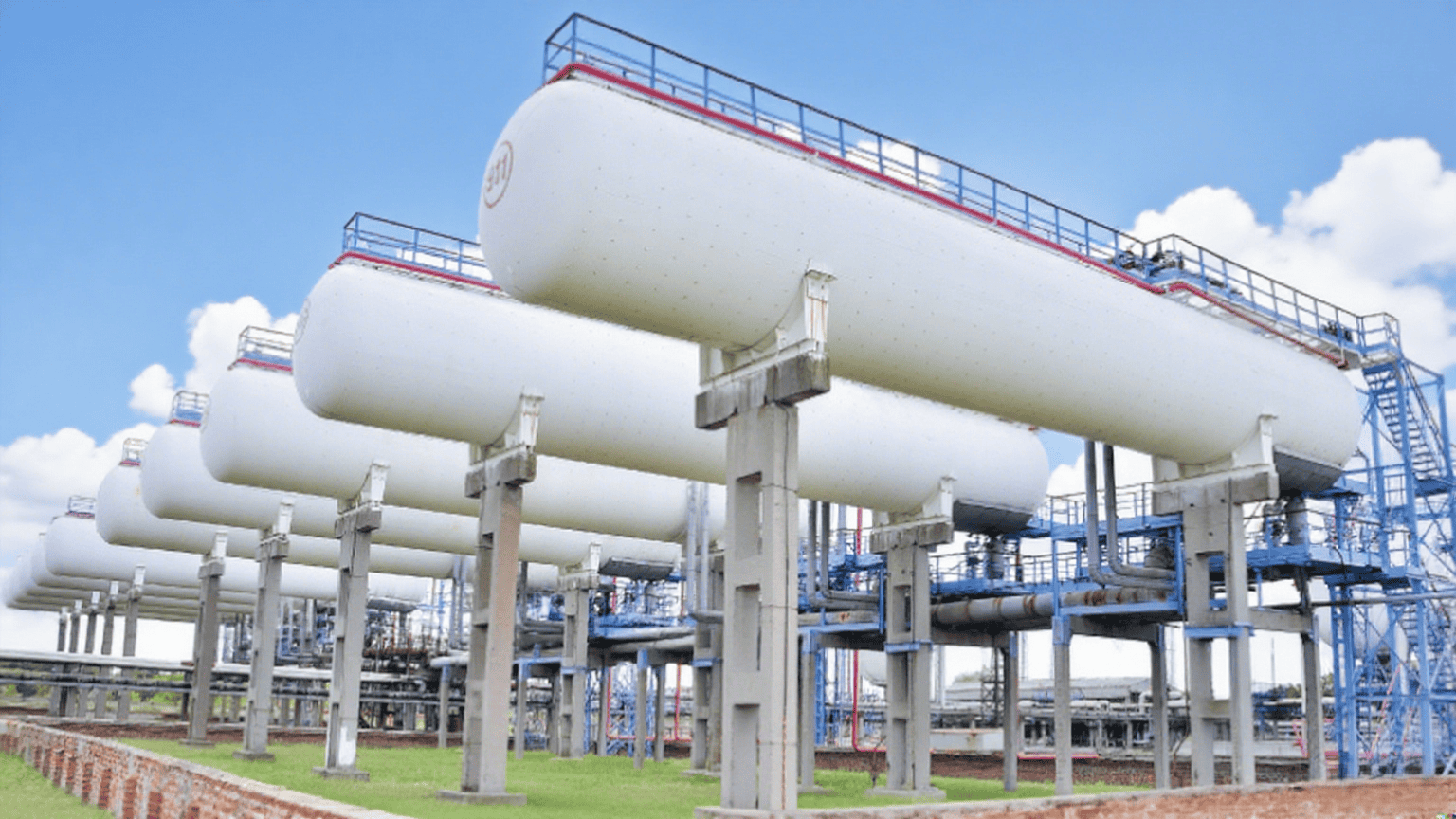

Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been cooled to around -162°C (-260°F), turning it into a liquid. This process reduces its volume by about 600 times, making it far more convenient and cost-effective to transport over long distances where pipelines are not available.
Why is LNG So Important?
Global energy demand continues to rise, yet the need for low-carbon solutions has never been stronger. LNG serves as a bridge between traditional fossil fuels and renewable energy by:
Reducing greenhouse gas emissions compared to coal and oil.
Enhancing energy security for countries without domestic natural gas reserves.
Providing flexible transportation options by ship or truck to remote areas.
What Are the Uses of LNG?
1. Power Generation
LNG is widely used in gas-fired power plants. Compared with coal, LNG can cut CO₂ emissions and particulate matter by up to 50%, making it an important transition fuel for nations seeking to lower air pollution and carbon intensity in the power sector.
2. Residential & Commercial Heating
In many regions, LNG is regasified (converted back into natural gas) and piped to homes and businesses for:
- Space heating
- Cooking
- Hot water supply
Its use is particularly valuable in urban areas, where cleaner fuels help reduce both indoor and outdoor air pollution compared to coal or biomass.
3. Industrial Applications
Heavy industries such as steel, glass, ceramics, and chemicals use LNG for high-temperature processes where consistent heat and energy efficiency are essential. The stable supply and lower emissions make LNG a highly attractive alternative to oil-based fuels.
4. Transportation Fuel (LNG Refueling for Vehicles & Ships)
Maritime sector: LNG helps shipping companies comply with the International Maritime Organization (IMO) 2020 sulfur emission regulations, cutting sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) emissions by up to 90%.
Trucking: LNG-powered trucks are increasingly favored for long-haul transport due to lower fuel costs and reduced emissions compared with diesel.
5. Emergency & Peak Shaving Supply
LNG serves as a backup energy source during periods of peak demand or pipeline disruptions. Utilities store LNG in large tanks and regasify it during winter demand surges or supply shortages.
6. Energy Exports & Global Trade
For gas-rich countries such as the United States, Qatar, and Australia, LNG makes it possible to export energy to distant markets beyond pipeline reach. This makes LNG a critical tool for energy diplomacy and balancing global energy markets.
Environmental Benefits of LNG
| Metric | LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas) | Coal | Oil |
|---|---|---|---|
| CO₂ emissions | Lower (approx. 50% less) | Very high | Medium |
| SOx/NOx emissions | Extremely low | High | Medium |
| Energy density | High | High | Medium-High |
| Transportation | Liquefaction allows long-distance shipping | Not suitable for long distance | Pipelines or tankers |
| Storage safety | High (non-corrosive) | Low | Not suitable for long distances |
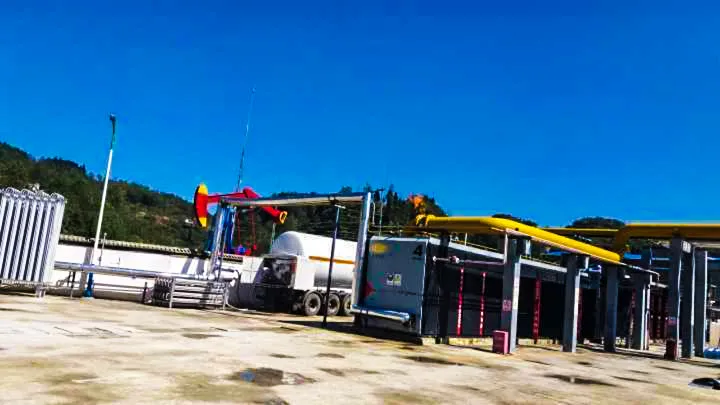
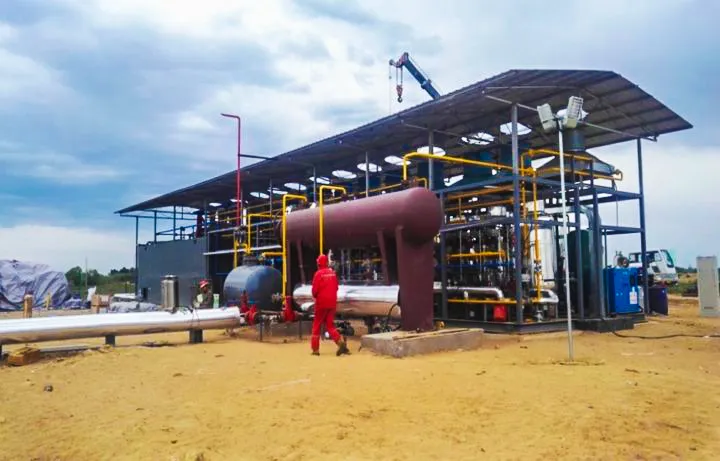
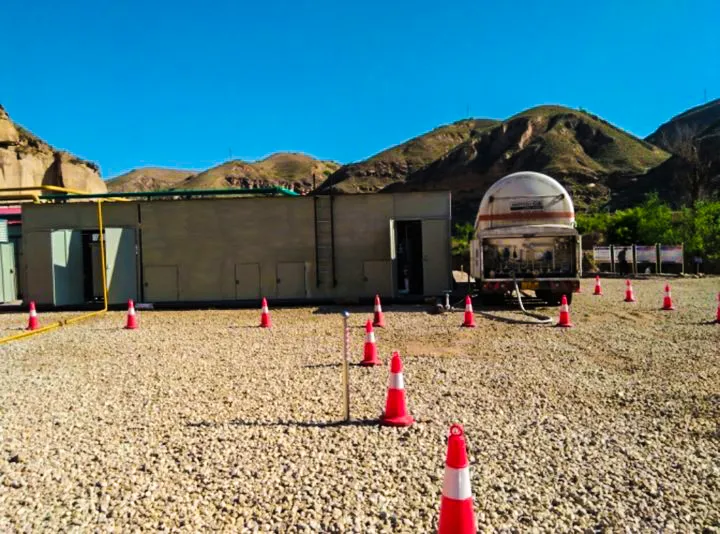
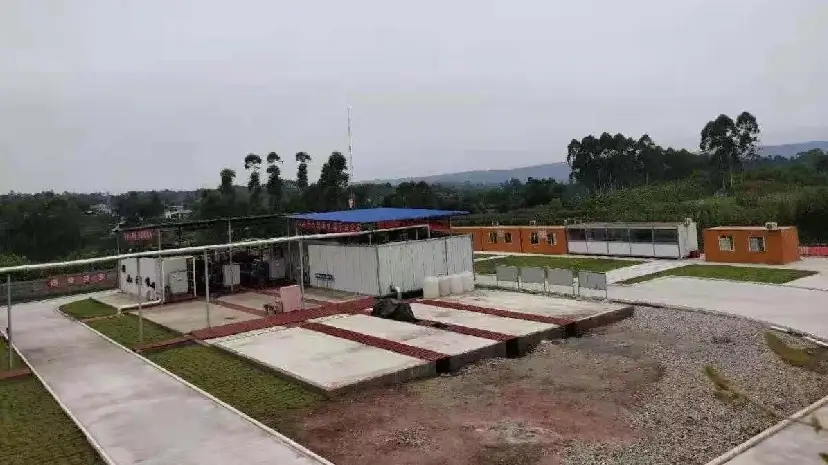
KAITIANGAS: Your Partner in Distributed Natural Gas Recovery
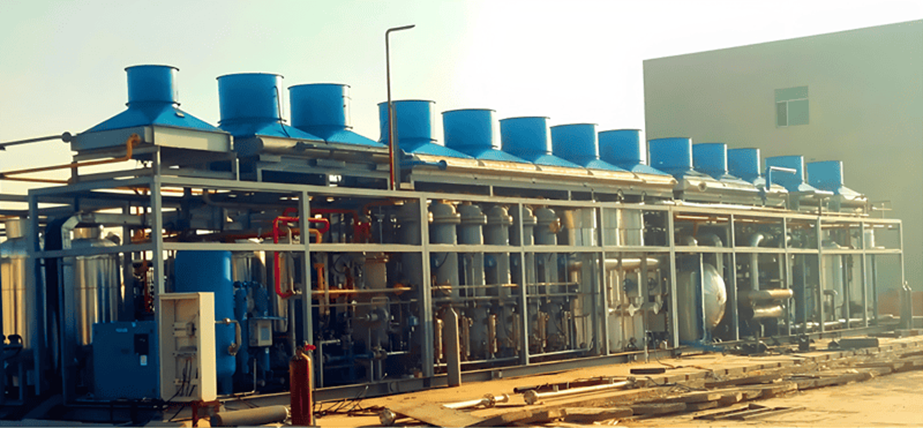

Founded in 2002, KAITIANGAS specializes in the recovery and processing of distributed natural gas resources. The company focuses on developing LNG recovery and liquefaction technology and equipment, engineering design, and global project implementation.
With proprietary intellectual property, mature system solutions, and a professional team, KAITIANGAS has successfully built and operated multiple wellhead LNG recovery projects in China, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia, gaining extensive on-site experience and strong technical expertise.
Conclusion
Liquefied Natural Gas plays a critical role in today’s energy systems—powering homes, fueling industries, driving ships and trucks, and enabling transoceanic energy trade. With its versatility, cleaner combustion, and global availability, LNG is set to remain a cornerstone in the transition to a low-carbon future.