What Is Natural Gas Used For?
What Is Natural Gas?
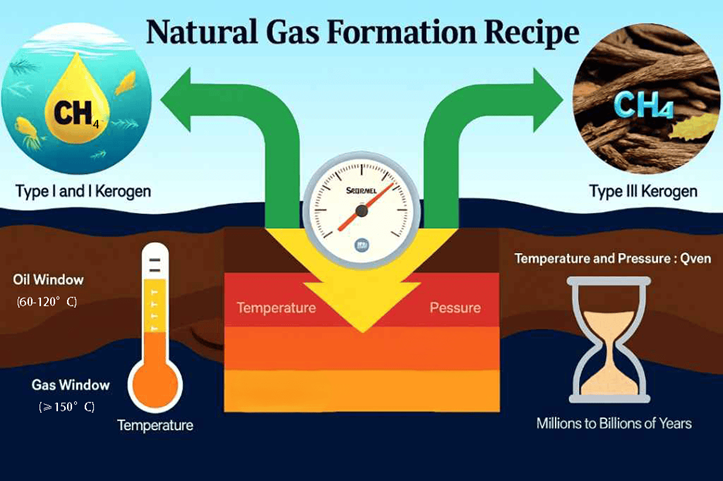
Natural gas, a fossil fuel that results from the decomposition of organic matter over millions of years, is usually trapped within deep rock layers. The primary component is methane (CH₄), often with smaller quantities of propane, ethane, and butane.
In comparison to oil and coal, natural gas releases fewer emissions when burned, emitting less carbon dioxide and nearly no particulate matter. This lower profile is the reason it is often marketed as a bridge fuel during the move towards renewable energy.
What Is Natural Gas Used For?
Power Generation
One of the most important uses for natural gas is the generation of electricity. Modern gas-fired power plants are extremely efficient and can quickly adjust output, making them perfect for managing intermittent renewable energy sources such as solar and wind. In a number of countries, natural gas has taken over coal as the primary energy source, dramatically decreasing air pollution and carbon dioxide emissions.
Heating and Cooling
In commercial and residential environments, natural gas is used to provide heat, hot water, and cooling. In colder regions, households depend on gas furnaces and boilers for warmth, whereas industrial and commercial establishments use natural gas to create steam to heat processes.
Industrial Applications
Natural gas is essential to industrial production. It is a feedstock used to make hydrogen, methanol, and ammonia-based fertilizers that support the global agricultural sector. Energy-intensive industries such as glass, steel, and cement rely on natural gas both as an energy source and a heat source.
Transportation
The transportation industry is increasingly using natural gas, particularly Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) and Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG).
- CNG is popular for taxis and buses, providing an alternative to diesel and gasoline.
- LNG, with its higher energy density, is commonly used in long-haul trucking and shipping.
Everyday Residential Uses
In the home, natural gas is used to power cooking appliances, dryers, and water heaters. Usage patterns vary by location: in developed nations, pipelines offer reliable access, while in developing economies, bottled small-scale LNG is more common.
Environmental Impact of Natural Gas Use
Natural gas is less polluting than other fossil fuels; however, it still comes with environmental challenges:
Lower CO₂ emissions: Natural gas burning produces about 50% less carbon dioxide than coal, and 30% less than oil.
Methane leaks: Methane, the principal component of natural gas, is a potent greenhouse gas—over 25 times more powerful than CO₂ in trapping heat. Leaks during extraction, storage, and transportation undermine climate benefits.
Transition fuel dilemma: While natural gas helps integrate renewable energy, overreliance may slow down adoption of sustainable energy sources.
The Economic Value of Natural Gas
The natural gas industry creates significant economic value worldwide:
Supply chain and employment: Exploration, production, distribution, and transport provide millions of jobs globally.
Geopolitics and international trade: Exports, especially LNG, influence global energy security and reshape political landscapes. Countries with abundant reserves hold strategic advantages.
Price fluctuations: Global gas price changes directly affect electricity costs, manufacturing efficiency, and household energy bills.
Natural Gas and the Energy Transition
Natural gas is often referred to as the “transition fuel” toward a low-carbon future.
Bridge to renewable energy: Gas plants ramp up quickly, complementing intermittent renewables such as solar and wind.
Future technologies: Existing natural gas infrastructures can be adapted for hydrogen production and integrated with carbon capture and storage (CCS).
Decarbonization potential: Although not a long-term solution, natural gas helps stabilize energy supplies as renewable energy continues to expand.
KAITIANGAS: Your Professional Partner for Distributed Natural Gas Recovery
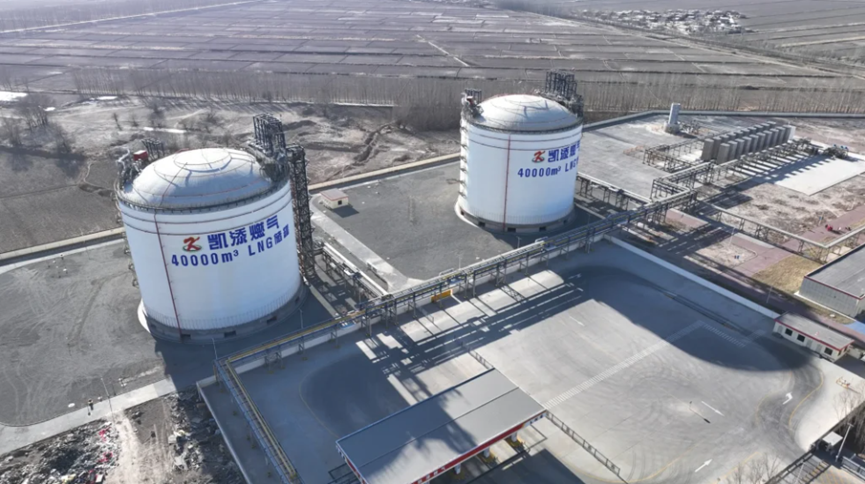

Founded in 2002, KAITIANGAS specializes in the recovery and treatment of distributed natural gas resources. The company focuses on the development, engineering design, and global promotion of distributed natural gas recovery and liquefaction technologies and equipment. KAITIANGAS holds independent intellectual property rights, mature system solutions, and a professional team, and has successfully built and operated multiple wellhead LNG recovery projects in China, the Middle East, and Southeast Asia, accumulating extensive on-site experience and technical advantages.
Conclusion
What is natural gas used for? The answer is everywhere. From heating and power generation to transportation, industrial production, and household use, natural gas is essential to modern life.
The environmental and economic impacts, however, are complex. On one side, natural gas reduces emissions compared to oil and coal. On the other, methane leakage and dependence raise climate concerns. As the world transitions toward sustainable energy, natural gas will remain an essential—though temporary—pillar of global energy security.